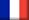
Projected Concrete
When to use projected concreteProjected concrete may substitute a number of techniques where low (<1m) to more substantial thicknesses (>0,50m) are required. These types of veils are frequently used in underground works, nailed walls or berlinese walls, retaining walls, embankment protection, external reinforcement structures… The mechanics of projected concreteProjected concrete works display roughly the same features as any other concrete works.
The advantages of projected concrete :When compared with concrete casings, projected concrete displays several advantages: ResistanceProjected concretes are generally nearly as resistant as concrete casings. 30 Mpa values are easily attained. |
Different ways of projecting concreteThere are two types of projection : One or several coats of projected concrete may be applied, depending on the required thickness and iron framework. Iron frameworksIron reinforcement elements are used to compensate the traction strains affecting the concrete section. They may be necessary to compensate shear strains when the concrete section does not suffice to do so. When producing a concrete veil, the iron framework is usually made of several layers of wire mesh welded together. Round iron bars may be used to further strenghthen the iron structures. Localized reinforcements are applied as ponctual strains warrant, when the latter exceed the resistance of the concrete section. |
Lost casingsProjected concrete may be applied to lost casings, which makes it possible to create evenly-shaped retaining works. Projected fiber-reinforced concreteFor iron frameworks, armatures are replaced by metal fibers of the appropriate type, which are added directly to the cement-aggregate mix prior to projection. This technique is particularly useful when applied to works with an extremely uneven layout where installing armatures and wire meshes appears difficult and of dubious efficacy. |
"Applying projected concrete to newly shaped embankments in a record time makes it possible to ensure temporary skin stability and weather protection, which are indispensable requirements when nailing operations are to be carried out." |
Conventional typical valuesProjected concrete works generally have low thicknesses. In the case of nailed walls, veils are generally 15 to 30 cm in thickness and have two layers of welded wire mesh. Important noteAny construction site must have a drainage system and meet the necessary requirements in terms of foundations and stability in order to ensure its durability.
|
|||
Keep in mindthat a study of the types of concrete needed is indispensable to ensure the durability of the projected works.